Molten or fused salt technology includes some very diverse applications. Interest in the use of molten salts in industrial processes is continually increasing and these media are gradually becoming accepted as a normal field of chemical engineering. In the heat treating industry, molten salts are commonly used as amedium for heat treatment of metals and alloys as well as for surface treatment. In nuclear and solar energy systems, they have been used as a medium for heat transfer and energy storage. Other applications include extraction of metals and high-temperature batteries and fuel cells.
All of these technologies are linked by the general characteristics of molten salts:
- Good heat transfer capacity
- Can attain very high temperatures (> 700°C)
- Can conduct electricity
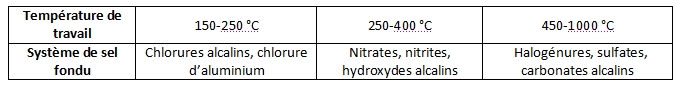
Molten salts have been used in many industries as a high temperature heat transfer medium. Depending on the temperature needed for a specific application, the molten salts can categorized as showed in the following table :
The steam production of steam in solar thermal power plants is a good example of how molten salts can be used as heat transfer fluids (see following figure):
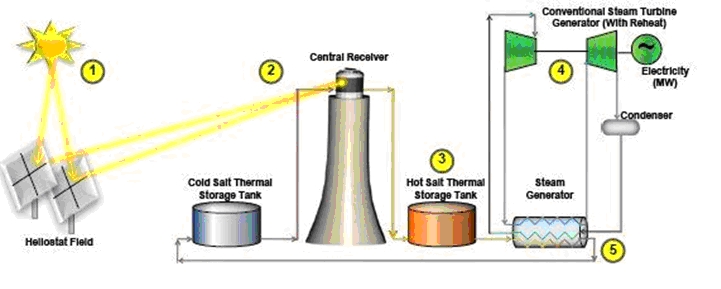
Operating at near atmospheric pressures reduces the mechanical stress endured by the system, thus simplifying aspects of design.
The containment material, which is in contact with the molten salt, is sometimes subject to corrosion. However the corrosion rate is strongly related to the type of molten salt, to the operating temperature as well as the velocity of the fluid. A coted alloy maybe needed.