Caprolactam is an organic compound, this colourless solid is a lactam or a cyclic amide of caproic acid. Approximately 4.5 billion kilograms are produced annually. Caprolactam is the precursor to Nylon 6, a widely used synthetic polymer. Firstly, Caprolactam was prepared by the cyclization of ε-aminocaproic acid, the product of the hydrolysis of caprolactam. Given the commercial significance of Nylon-6, many methods have been developed for the production of caprolactam :
Most of the caprolactam is synthesised from cyclohexanone, which is first converted to its oxime. Treatment of this oxime with acid induces the Beckmann rearrangement to give caprolactam.
The immediate product of the acid-induced rearrangement is the bisulfate salt of caprolactam. This salt is neutralized with ammonia to release the free lactam and cogenerate ammonium sulfate. In optimizing the industrial practices, much attention is directed toward minimizing the production of ammonium salts.
The other major industrial route involves formation of the oxime from cyclohexane using nitrosyl chloride. The advantage of this method is that cyclohexane is less expensive than cyclohexanone.
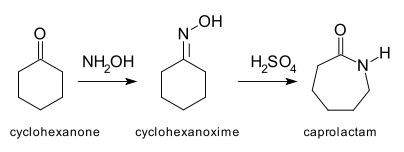
The immediate product of the acid-induced rearrangement is the bisulfate salt of caprolactam. This salt is neutralized with ammonia to release the free lactam and cogenerate ammonium sulfate. In optimizing the industrial practices, much attention is directed toward minimizing the production of ammonium salts.
The other major industrial route involves formation of the oxime from cyclohexane using nitrosyl chloride. The advantage of this method is that cyclohexane is less expensive than cyclohexanone.